Is the Planet closest to Earth? It probably is different from the one that you’re considering.
Recently, there needed to be more clarity about which Planet in the Solar System is closest to Earth.
The order in which the planets are placed within the Solar System, moving outwards away from the Sun, stays the same.
Earth is home to Venus, the second Planet inwards toward the Sun, and Mars is the Planet to be pushed outwards by the Sun. In both cases, Venus comes closer to Earth than Mars when they are at their earliest approach. Therefore, it’s still accurate to state that Venus is closest to Earth than any other planet.
Bright Planets. Planets that are Observable by the Naked Eye
Understanding why planets are bright at night, it’s easy to comprehend why the planets visible from Earth are closer to the Sun and further away from us.

Five planets can be observed from Earth with no help from telescopes. They can be observed throughout the year; however, generally, it is only possible to observe some of them at once because their orbits may be to the back of the Sun, which can block the view or be too far from Earth. Because they can be seen easily, provided you know what you’re seeking, sometimes they are called bright planets.
The brighter planets are ordered by proximity to the Sun. They are:
- Mercury
- Venus
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
Venus Mars and Venus Mars are easy to comprehend since they are neighbours and right next to the Sun. Venus is the closest Planet to us and the third most bright celestial object in the sky; the Sun and Moon are just behind it.
What’s the closest Planet in the Solar System, Earth? But not Venus Scientists Say

Even though Venus is the one closest to Earth in its whirlwind in orbit of Earth, Mercury is the Planet that stays closest to Earth the longest, as per the commentary published on Wednesday (March 12, 2013) in the journal Physics Today.
“Because of a lapse in ignorance, carelessness or groupthink, scientists and propagandists have disseminated knowledge using a flawed belief in the distance between the planets.”
Solar System and Planets
The solar system comprises the Sun and everything else that revolves around it. The revolution occurs under the pressure of gravity. Additionally, moons, planets, asteroids, comets and meteoroids rotate around the Sun.
A division between the 8 planets is divided into four more minor planets and the four planets with larger sizes. In addition, the four planets with smaller sizes are called the terrestrial planets. This is because they are solid as the Earth. The four largest planets, however, have gas giants. This is because they comprise mainly methane and a metal rock core.
PLANETS OF TYPES IN SOLAR SYSTEM
The four planets close to the Sun and the Sun’s four planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars- are frequently described as “terrestrial planets” because their surface is sand. Pluto Also has a hard, though frozen and icy, surface but has not been included in the terrestrials.
The four major outer planets which include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune These are known as Neptune Saturn, Uranus and Jupiter, are sometimes referred to as the Jovian and “Jupiter-like” planets due to their size in comparison to terrestrial planets. They’re also made up of gases such as ammonia, hydrogen and helium instead of hard surfaces, though scientists believe one or more of them might contain solid cores.
Jupiter and Saturn are often referred to as the gas giants, while further, far away, Uranus and Neptune are often called the giants of the ice.
What’s the Planet closest to Earth?
The common sense solution is Mars or Venus as our neighbours to the north. Of both, Venus comes closer to the Earth than any other planet, and its orbit is also closest to our own. But, as an article from Physics Today points out, more than half of the time, Venus isn’t the closest Planet. Mercury is.
The scientists responsible for this article analyzed the data and discovered that, on average, Mercury is the closest Planet to Earth and every other Planet within the Solar System. Trippy.
Scientists developed a solar system model that includes every Planet that moves around the Sun’s orbits. The planets circle over thousands of years while measuring the distance between the two. Scientists then averaged those numbers to determine which planets are closest to one another over time.
Simple, but not right
To determine the distance average between the two stars, The Planets and other websites assume that both orbits are coplanar. They subtract the diameter of the orbit’s inner circle (r1), the same as the average radius for the outer orbit—the radius r2. The distance between Earth (1, the astronomical unit to one astronomical unit to the Sun) and Venus (0.72 AU) is 0.28 AU. The table at the end of this article displays the distance calculated between the two planets using this method.
It may seem intuitive that the distance between the points on two concentric ellipses will represent the variation in radius. However, the actual differences only determine the average distance between the closest points of ellipses. When Earth and Venus are on their closest to each other, their distance is about 0.28 AU. This is the only Planet that gets closer to Earth. However, both planets often are at their farthest distance, as Venus is on the other side of the Sun, which is opposite Earth, 1.72 AU away.
What planets are visible from Earth?
BY ELENA STONE, MARCH 27, 2022, 8 MINS READ
For those who aren’t experienced in the sky at night, it is counterintuitive to consider planets as objects that could be observed easily from Earth without the aid of binoculars or telescopes. We typically consider planets as dim pieces of gas and rock that orbit the Sun and stars as bright objects. It could be a surprise to learn that planets can be observed from Earth nearly every night and sometimes even during the day.
Six planets are visible from Earth by an eye. For an extended period, ancient astronomers believed that these objects were star-like. They believed that the Latin word Greeks used to identify them was planetary. It is a reference to “wanderer”, and for a long time, they were confused about why they differed from stars and believed that these planets could be the most unique in the Solar System.
Which is the closest Planet to Earth?
But Venus is only the closest Planet when it lies between Earth with the Sun during its revolution. If Venus occurs on the opposite side of its orbit, then Earth, Mercury, for the majority of time, is thought to be the closest. The distance between Mercury and Earth currently is approximately 33 million miles.
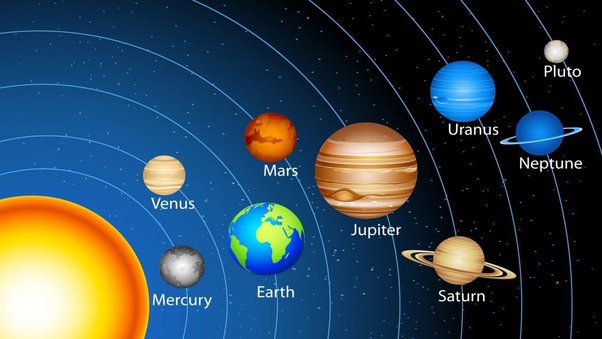
Which are the Planets of the Solar System?
At one point, people believed that Earth was the central point of the Universe as it was the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars centred around us. It was only after years of continuous observations and the development of instruments that astronomers began to recognize that we’re, in reality, a part of the more extensive system of planets centred around the Sun. It’s only in the last century that we’ve been able to realize how vast the Solar System is.
We are still studying. In the last couple of decades, the totality of celestial moons and bodies thought to revolve around the Sun has increased. We also have begun to debate what constitutes a “planet” (a debated issue indeed!) and have introduced new classifications such as dwarf planets, minor planets, plutoids and so on. to reflect discoveries made. How many planets exist, and what’s unique about them? Let’s look at them one at a time, will we?
Mercury:
Mercury is the closest Planet When you travel outwards away from the Sun. It orbits around the Sun at about 58 million kilometres (36 million miles). Mercury is arid, therefore, without a significant atmosphere to absorb its heat. As such, it can experience significant temperature variations. The side facing the Sun can reach temperatures 425 deg C (788 deg F). Then the side in shadow is lower to -173 degrees Celsius (-279.4 degrees Fahrenheit).
Exploration and Exploration Activities:
The exploration and study of Venus has been a challenge in the past due to the intense atmosphere and harsh surface. The Planet’s surface has been mapped recently because of the advent of radar-based imaging. But, numerous robotic spacecraft and a few landers have completed the journey and learned more about the Earth’s closest neighbour.

The Soviets launched the first attempts in the 1960s through the Venera Program. The original mission (Venera-1) was unable to succeed because of the loss of contact and contact; the second (Venera-3) was the first artificial object designed by humans to penetrate the atmosphere and impact the surface of a planet (on March 1, 1966).).
NASA also conducted similar missions as part of its Mariner program. The Mariner 2 mission, launched on December 14, 1962, was the first interplanetary successful and was just 34,833km (21,644 miles) from Venus, the Planet’s surface. Between the late in the 60s and into the mid-70s, NASA carried out several flybys with Mariner probes, such as that of the Mariner 5 mission on October 19, 1967, and that of the Mariner 10 mission on February 5, 1974.
Venera-7 was the most famous. Soviets launched six additional Venera probes between the late 60s to 1975 and four additional missions at the end of the 70s and the beginning of the 1980s. Venera-5, Venera-6, as well as Venera-7 all were able to enter Venus’s atmosphere and send vital data to Earth. Venera 11, as well as Venera 12, were able to detect Venusian electrical storms. Venera 13 and Venera 14 came to rest on Venus and took the first photos in the colour of Venus’ surface. The mission was completed in October 1983, at which point Venera 15 and Venera 16 were positioned in orbit to map the Venusian terrain using synthetic aperture radar.
In the latter part of the seventies, NASA started with the Pioneer Venus Project in the late seventies, which comprised two distinct missions. The first mission was The Pioneer Venus Orbiter, which placed itself in space on Venus (December 4 1978) to study the atmospheric conditions and map its surface. The second probe, the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, released four probes into the atmosphere on December 9. 9th in 1978. They returned data about its composition, winds as well as heat exchanges.