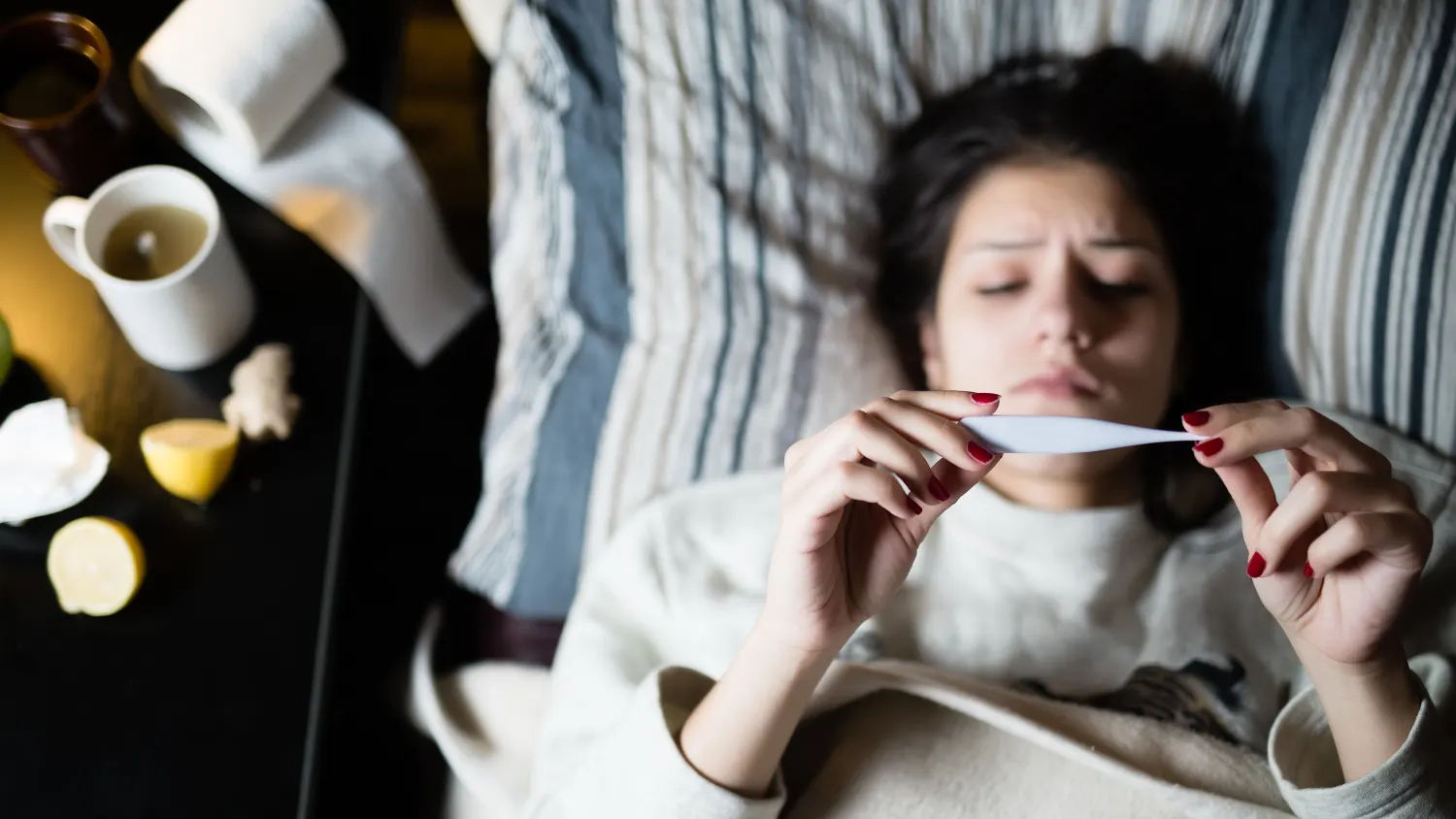
Seasonal flu is a serious respiratory illness caused by influenza virus that can be found throughout the globe. This is an all-year-long illness impact. It is a cause of diseases that vary in severity. Sometimes, it can cause hospitalization or even death.
Most patients recover from symptoms such as fever within one week and do not require medical treatment. In the event of an outbreak, it can result in fatal illness or death, especially in high-risk groups, which include the highly young, elderly hea, healthcare workers, pregnant women, and people with severe health conditions.
In climates with temperate temperatures season,nal outbreaks typically occur during winter. In tropical zones, flu can happen yearly, creating more irregular episodes.
Everyone is sick today.
Social isolation helped keep seasonal infections at bay in the last two years. Then they’re back.
The number of positive tests for influenza within the United States stood at 25 percent at the end of November, as per the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, compared to 8 percent during the same point in 2019. Respiratory syncytial viruses (RSV) have brought the capacity of some hospitals for children to. Also, Covid hospitalizations have been rising. The tripledemic experts in epidemiology feared the viruses, along with several other seasonal, recurring ones, have joined forces to cause the onset of a series of running noses and fevers. Therefore, if your children, colleagues, and anyone you know feel sick, it’s because of.

“This season is unique,” says Katelyn Jetelina, the author of Your Local Epidemiologist, a publication about the spread of infectious diseases. The high rate of influenza-like illnesses could signal the beginning of a peak or a warning sign of a devastatingly tricky season. “How much it’ll rise, as well as how severe the effects will be, is something that we wait to see,” she says. “We’re dependent on the clock.”
Symptoms and types of viruses
There are millions of viruses throughout the world. They are spread by coughing or sneezing on the affected surface or drinking a drink infected with bacteria. Certain types of viruses are more frequent in winter, including influenza, RSV, and parainfluenza. rhinovirus, norovirus and coronavirus. This includes COVID-19.
Doctors can check for and recognize only a few viruses. Many viruses have no name. Therefore, it is impossible to pinpoint the exact virus that causes those painful aches and sneezing.
If you notice any signs, such as a headache, your doctor or local CityMD will be able to help. See any of our doctors, get a diagnosis, and be given timely treatment guidance. The evaluation is critical to rule out COVID since some symptoms could appear similar to viral infections like the common cold.
The most common symptoms of a virus are:
- Nasal congestion and sneezing
- The throat is swollen
- Coughing
- The body is aching and tired.
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
It’s tempting but needs to be a more helpful concept.
One of the theories that have been circulating is the notion of an “immunity debt,” which is the idea that since most of us have been spending the last two winters socially distancing or being locked in a lockdown, fewer interaction with others has made our immune systems at risk as natural infections do not prepare them.

The treatment of common cold
The most effective way to deal with the cold is to follow the same thing that has always worked. “Try to avoid other people and limit your exposure within you,” Dr. Vyas recommends.
- Do not enter spaces that are crowded or enclosed.
- Make sure to cover your mouth using your hands or the inside of your elbow when coughing.
- Discard tissues following use.
- Cleanse your hands often.
- If you’re capable.
Singularity and Health
Another method is vital to combat viruses. “Get your flu shot and the COVID-19 vaccine,” Walter advises. They’re safe and reliable means to shield yourself from harm and those in your vicinity.
Remember to immunize your kids, as well. This is the most effective way to safeguard your health. COVID-19 is currently recommended for all people five and over.
Flu vaccines are advised for anyone aged six months or over. Flu vaccines are made to shield against the different types of influenza virus that researchers anticipate to be present throughout the year.
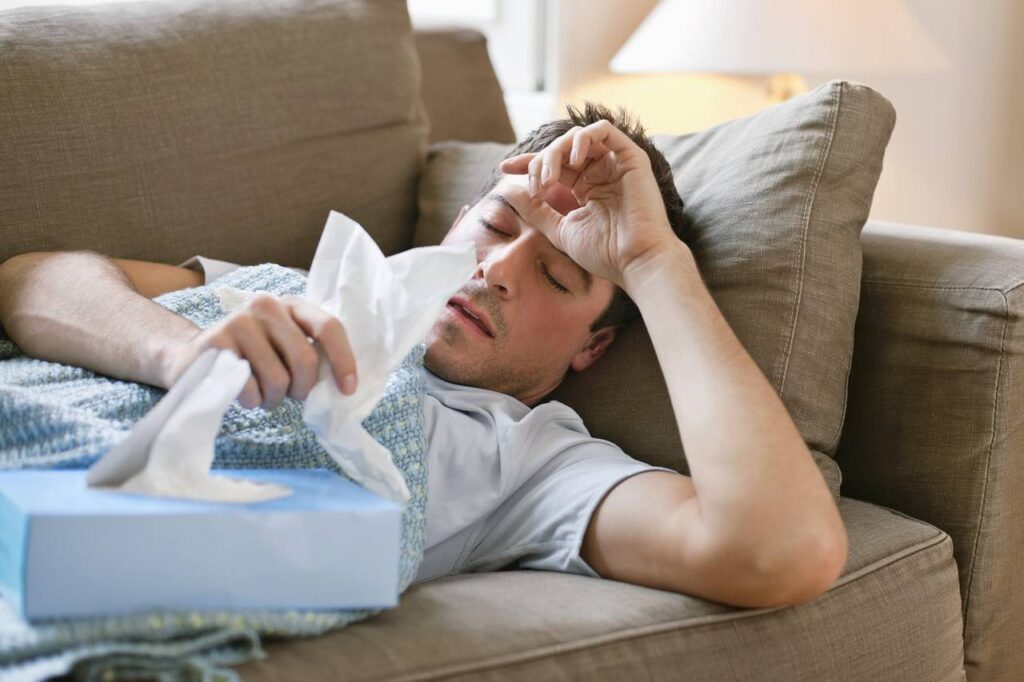

Researchers such as Walter and many others are working on developing influenza vaccines that are more durable and provide excellent protection against various strains of influenza.
How Come It Feels Like All People Are Sick?
New York. NY (November 23rd, 2022) Waleed Javaid, MD, speaks about the current virus surge and ways individuals can avoid getting sick. According to him, “There’s the feeling that we’re in the middle of a dazzling epidemic of viruses in the aftermath of an increase in the frequency of training without coronavirus protection; RSV and the flu are experiencing peak numbers more quickly than we anticipated. In addition, experts caution that COVID-19-related cases are set to increase with the Christmas season approaching. If we look at flu, the primary issue is that (compared to the previous year) the rate is more prevalent and much sooner than we were. It’s not like anyone is noticing the fact that.
Who are the people who are more prone to illness?
The general rule is to look at three major elements. The first is genetic susceptibility. You’re born with a predisposition genetic for being infected with more ease. There could be inborn mistakes like polymorphisms within genes well-studied to protect the host.
Another is the environment where the burden of disease is high. When you consider our ancestral ancestors’ lives, lots were dead before they reached fifty years old because they suffered from a higher antigenic load (the quantity of inflammation stress that an infection can cause] before the introduction of vaccinations, better living standards as well as better sanitation.
Did COVID-19 weaken our immune systems?
This is also theoretically plausible. However, it’s not the entire explanation, according to Dr. Duane Wesemann, a researcher in the field of antibodies at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The immune system tracks its exposures via antibodies, which means that COVID-19 likely altered the way it records exposures in some manner. It’s also strong enough to withstand a couple of years of isolating, Wesemann said.
COVID-19 poses a greater risk than the flu, RSV, or common cold. The doctor said it seemed sensible to take precautions from it even though it could have rendered us a little more susceptible to less severe illnesses.