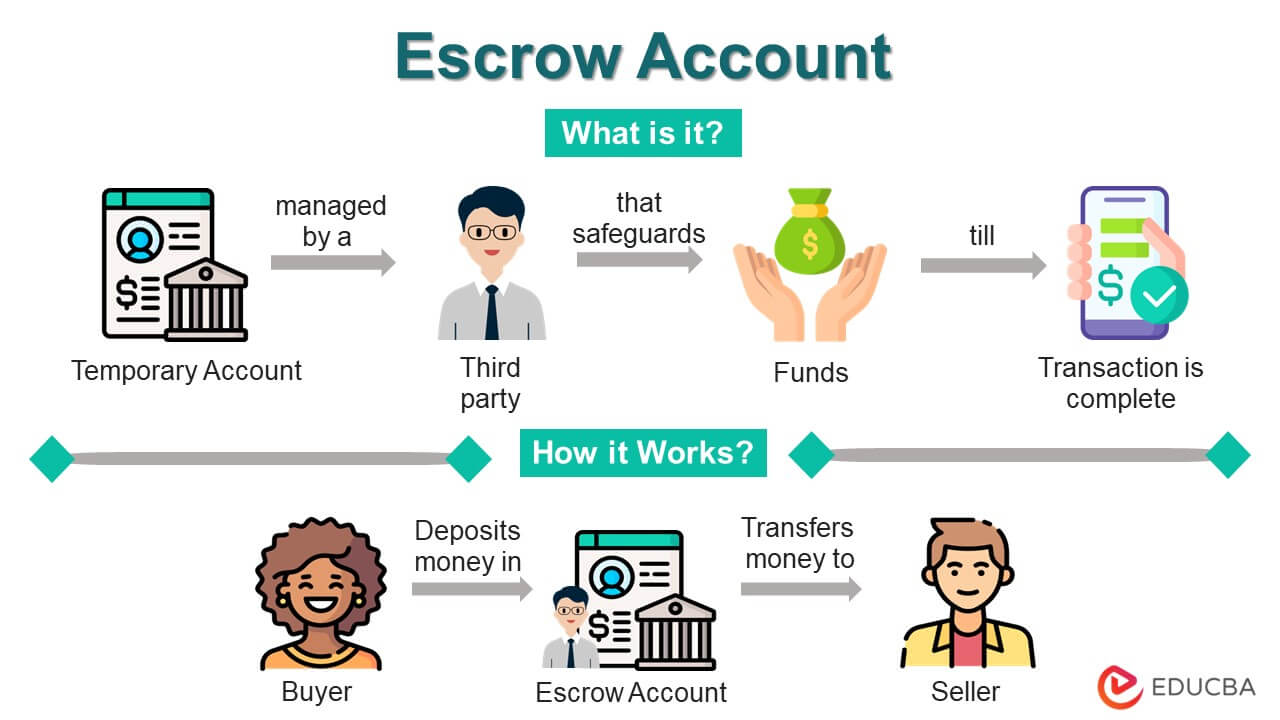
Each computer has RAM, which is utilized for computational operations. Random Access Memory is a device that runs on hardware with a quick, short-term, volatile memory. In this post, we will help you understand RAM compatibility and the essential details you must be aware of.
The most effective method of determining the compatibility
There are so many types of memory that it’s crucial to determine which one works with your device. This is where our simple-to-use compatibility tools come in.
The Crucial System Scanner is an online tool that easily researches compatible memory. The tool analyses your computer’s configuration and will automatically suggest a compatible upgrade within moments. This tool is useful if you need more clarification on your PC’s specifications.
The Crucial Advisor can be described as software that lists compatible upgrade options for the system you have installed after you’ve given the information regarding your system’s manufacturer, model, and year of manufacture. Use this tool only if you have your computer’s specs.
If you have one or both of our tools for compatibility, we’ll perform the compatibility analysis for you. Memory upgrades are among the most straightforward methods to improve the performance of your PC. It can be as easy to install it!
When you utilize one of the tools for compatibility and purchase through Crucial.com, We promise compatibility, or we’ll refund your purchase.
RAM is usually used to mean SDRAM
When we talk about RAM, typically, we’re talking in terms of Synchronous Dynamic RAM (SDRAM). This article focuses on, as well. In most laptops and desktops, RAM will appear as a small stick that you connect to the motherboard.
There is a growing demand for ultra slim and light laptops with the RAM connected to the motherboard directly to save space. This does not mean that it is less upgradable and can be repaired.
Beware of confusion between SDRAM and SRAM, which is Static RAM. Static RAM is a memory that’s utilized for caches in CPUs as well as other functions. It’s faster. However, it is also limited in capacity, which makes it ineffective as an alternative to SDRAM. You are likely to encounter SRAM when you use it in the normal course of your life; therefore, it isn’t something to be concerned about.
Types
Two of the most popular forms of modern memory are static RAM (SRAM) as well as Dynamic RAM (DRAM). In SRAM, the majority of information is saved together in the current state of a 6-transistor memory cell, generally together with MOSFETs with six. SRAM costs more to make. However, it’s generally more efficient and consumes less energy than DRAM. Modern computers use SRAM, which can be used to cache memory in the CPU. DRAM is a storage device that stores information with the transistor and capacitor pair (typically MOSFET and MOS capacitor, respectively),[27th together form the DRAM cell. The capacitor can hold either a low or high charge (1 or zero, depending on the). At the same time, the transistor is a switch that lets the circuitry controlling the chip determine the capacitor’s charge or modify the charge state. Since this type of memory is cheaper to manufacture than traditional RAM, it’s the most common memory used by modern computers.
Both types of RAM can be regarded as volatile because their states are lost or reset after power is cut off out of the device. However, read-only memory (ROM) is a storage device that stores information permanently by enabling or deactivating certain transistors so that it cannot change. Write-able ROM variants (such as EEPROM or NOR flash) have the same properties as RAM and ROM, which allow data storage indefinitely without power and update without requiring any special equipment. ECC memory (which is available as SRAM or DRAM) has special circuitry that can find and correct any irregularities (memory mistakes) within the data stored, together with parity bits or error correction codes.
The phrase RAM refers to solely SSDs (DRAM or SRAM) and the primary memory used in many PCs. For optical storage, DVD-RAM can be an oxymoron since, unlike DVD-RW and CD-RW, it does not require to be erased prior. However, it behaves like a hard disc drive but is a little slower.
- Memory Cell
- Addressing
- Memory Hierarchy of Memory
Memory Form Factor
RAM modules are offered in two standard and primary forms:
Dual Inline Memory Module, also known as DIMM DIMM: The DIMM can be described as the RAM element used in desktop computer systems. DIMM is the physical dimension of the memory stick that is larger for desktop computers. The typical length for DIMMs is 133.35 millimetres for DIMMs.
Small Outline DIMM, also known as SO-DIMM. RAM modules are generally designed for laptops and compact computer systems. They’re about half the size of DIMMs, with only 67.6 millimetres in length.
Generation Or Memory Type
With the advancement of technology over time, RAM sticks have also developed and improved, gaining more options and functions.
Five main generations exist that are used for DDR SDRAM (Double DDR Synchronous Dynamic Memory), which are in common in the market currently:
- Version 2000: DDR1 SDRAM
- Release in 2003: DDR2 SDRAM
- Release 2007: DDR3 SDRAM
- 2014 Release: DDR4 SDRAM
- 2020 Release: DDR5 SDRAM
- There isn’t any backward or forward compatibility between the two RAM generations. It’s impossible to put one in the same slot as a different one since they have the same number of pins.
DIMM Slots Available
- In addition to capacity, your motherboard ought the capacity to hold extra RAM sticks.
- RAM sticks are installed on a Dual Inline Memory Modulator (DIMM) slot.
- Two slots are fully loaded on your computer.
- If you own the quad-channel motherboard (more about this in the future), you will likely have two slots open for adding additional RAM.
- If all slots are filled, swapping two sticks for larger-capacity ones is worth swapping.
- There is a possibility of upgrading one stick at a time; however, the dual stick setup will be faster.
- The reason will be explained later in this article.
What is the amount of extra RAM You Need?
You can use the Performance Monitor to understand better the amount of data your system is writing into virtual memory.
- Click Start, then enter “Perform” into the search field.
- Open Performance Monitor
- In the Monitoring Tools section, click to open the Performance Monitor.
- After that, press”+” in the middle of the green in order to create a more variable.
- Select the file you want to ping from the list, then click Add
- Watch the video and click OK.
Do I need to focus more on high or low latency? Clock speed?
The RAM module’s speed rating measures its transfer speed. “latency” refers to how quickly RAM modules connect to its hardware. The lower numbers will result in quicker data transfer. The more quickly RAM can access data, the faster data transfer to your processor. A higher capacity of RAM is considered greater, and a more rapid rate of clock is preferred compared to less RAM or with lower capacity and less latency.
It is important to remember that RAM is the simplest component for upgrading your computer. If you’re creating a PC for a low budget, go to higher capacity first if you must choose. It’s desirable to use two units rather than just one. More RAM may not be required based on the type of work. If you are gaming, you’ll have suitable memory with just 8GB. If you are with other programs which need to transfer data, 16GB or more could improve efficiency.
What are the reasons for considering a RAM upgrade?
Certain apps rely on the system’s RAM. The Chrome browser is known to be RAM-heavy since it considers each tab a distinct process that can allocate its memory. “Sandboxing”, which is what it’s known as, can be advantageous because if one of the tabs fails, it won’t shut the browser down. However, it’s a RAM-intensive process.
If you frequently use multiple browsers or application tabs running simultaneously, upgrading your RAM is an almost sure way to increase efficiency. If your computer runs slower than it is at any time, then the Task Manager within Windows can be a great way to see if you’re excessively consuming your RAM.
Start the Task Manager on Windows 10 (or Windows 7 or 8 on a legacy system) using the ALT + CTL + DEL keys.